PUBLICATIONS

|
Α.
TRANSITION FROM EDUCATION TO LABOUR MARKET
1. 2nd GRADUATES
SURVEY ,
(PDF file in Greek)
Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia
Vretakou, Athens 2008
ABSTRACT
The second graduates survey followed-up upper secondary education graduates (of school year 2000-01) from education to labor market. The survey was funded by the second "Operational Programme for Education and Initial Vocational Training" of the third "Community Support Framework". The scope of this survey, similarly with the1st Graduates Survey, was to generate and explore quantitative data on the transition
of secondary education (both general and vocational) students from school
to work. Since the time of the first graduates survey, after an educational reform, the configuration of upper secondary education had changed. The participants were graduates of a diversified upper-secondary education
cycle, which included a general education school (Integraded Lyceum) and a technical-vocational school (TEE). The 2nd Graduates Survey has following characteristics:
- It is composed of two parallel surveys which has been carried out at the same time.
- Participants of the first survey were graduates of technical-vocational schools (TEE) and participants of the other survey were graduates of general education schools (Integraded Lyceums).
- It is a longitudinal survey (panel) that has been carried out in two phases.
PHASES OF 2nd GRADUATES SURVEY |
Phase |
Year |
Graduates Survey (TEE) |
Graduates Survey (Integrated Lyceum) |
Α΄ Phase |
2001
(Spring) |
Representative nationwide sample of 11.629 undergraduates filled in questionaire in the classroom. |
Representative nationwide sample of 2.863 undergraduates filled in questionaire in the classroom. |
Β΄ Phase |
2007
(Autumn) |
Follow-up of Α΄ Phase sample. Telephone interviews. Respontents: 5.780 graduates |
Follow-up of Α΄ Phase sample. Telephone interviews. Respontents: 1.630 graduates |
The 2nd Graduates Survey
revealed the pattern of overall employment the
graduates of general and vocational schools. Moreover the survey revealed the extent of mached employment of TEE graduates. According to findings matced employment comes up to 35%. This figure raise question for the effectiveness of vocational
education in Greece.
2. LONGITUTINAL SURVEY OF EDUCATIONAL AND OCCUPATIONAL CHOICES OF SECONDARY EDUCATION STUDENTS (A΄ PHASE),
( ZIP file in Greek)
Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou, Athens 2008
ABSTRACT
The scope of the
survey is to identify the educational and occupational pathways of greek
youth and the infleuncing factors that shape their preferences over
time. This panel type survey was funded by the second "Operational
Programme for Education and Initial Vocational Training" of the
third "Community Support Framework" and has been planned to
have 3 phases. In A΄ phase (it has already been carried out in spring
2007), 6.727 gymnasium students (age 15) were asked about their future
educational and occupational plans (self-administered questionnaire).
Moreover, a variety of indexes were specified (school engagement, self
esteem, locus of control, social support) upon which their preferences
were tested. B΄ phase is scheduled to be carried out (personal interviews)
three years after A΄ phase (spring
2010), when most of the sample members would be in the final year of
upper secondary education (either general or vocational stream). The
final phase C΄ is scheduled to be carried out (telephone interviews)
five years after phase B΄ (spring 2015) when most of the sample members
would be either in tertiary education or in labor market.
3. 1st GRADUATES SURVEY ,
(file in
Greek)
Stamatis Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rouseas,
Vasileia Vretakou, Athens 2000
ABSTRACT
This survey was conducted
in the framework of a feasibility study on the establishment of a S-T-W
Observatorium at the Pedagogical Institute of the Ministry of Education
in Greece and was funded by the first "Operational Programme for
Education and Initial Vocational Training" of the second "Community
Support Framework". The scope of the survey was to generate and
explore quantitative and qualitative data on the transition of secondary
education (both general and vocational) students from school to work.
The students were graduates of a diversified upper-secondary education
cycle, which includes a general education school (GEL), a vocational
school (TEL), an occupation-specific school (TES) and an integrated
comprehensive (general and vocational) school (EPL). Only graduates
who did not continue their studies in post-secondary and higher education
were included in the survey. Compulsory education lasts 9 years and
it ends with the 3-yr lower-secondary general school (the Gymnasium).
The methodology followed for the survey may be identified as a cross-sectional
one with the use of structured personal interviews (carried out during
1998). The population of the cohort used was 75,600 graduates (of the
school year 1988-89) of all four types of school and the sample used
in the survey was 4,986 graduates (6.6%). The findings are presented
in the form of multiple entrance tables and graphs.
The national survey
revealed the pattern of overall employment and matched employment for the
graduates of all four types of school (and for all the specialties offered
within a certain type of school). Low matched employment rates for the graduates
mainly of TEL and EPL raise question for the effectiveness of vocational
education in Greece.
4.
TRANSITION FROM EDUCATION TO LABOR MARKET: FINDINGS FROM A LOGISTIC
REGRESSION ON DATA OF THE "1st GRADUATES SURVEY"
(PDF
file in Greek), Panagiotis Rouseas, Athens
2000
ABSTRACT
A logistic regression
analysis on data from the 1st Graduates Survey (dependent variable employment)
revealed that gender, primarily, work experience acquired while attending
school, and knowledge of a foreign language (in this order) seem to be the
most important factors which determine the employment status of secondary
general and vocational education graduates in the Greek labour market.
5. GRADUATES
IN THE LABOR MARKET: EVIDENCE AND CAREER EDUCATION POLICY ISSUES FOR
GREECE ,
(PDF file in English) [published
in "International Journal of Vocational Education and Training"),
Vol. 10, No 1, pp. 53-63, 2002]
Stamatis
Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou
ABSTRACT
Gender, primarily, work
experience acquired while attending school, and knowledge of a foreign language
(in this order) seem to be the most important factors which determine the
employment status of secondary general and vocational education graduates
in the Greek labour market. Evidence from a national graduate survey (1st Graduates Survey) shows that employment mismatch, earnings and unemployment period
following graduation are differentiated unfavorably for women, and favorably
for individuals who held a job while attending school, and for those who
were certified in a foreign language (mainly in English). School-based career
education policy measures such as a more efficient informing of students
on labour market conditions, and linking schools with local enterprises
through alternating (school-industry) enterpreneural activities, would raise
the quality of the vocational orientation of the students and enhance their
opportunities to secure matched employment upon graduation.
6.
UPPER SECONDARY CURRICULUM OPTIONS AND LABOR MARKET PERFORMANCE: EVIDENCE
FROM A GRADUATES SURVEY IN GREECE,
(PDF file in English), [published in "Journal of Vocational Education and Training", Vol.
54, No 2, pp.295-304, 2002]
Stamatis Paleocrassas,
Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou
ABSTRACT
This paper presents
empirical evidence from the 1st Graduates Survey and discusses labor market performance
of graduates from curriculum options in a diversified upper secondary education
scheme, with emphasis on the benefit of choosing the vocational intensity
of instruction. Such evidence, which was generated for the Greek education
system, shows a generally high employment mismatch (68%-85%), the largest
mismatch attributed to graduates from an integrated-comprehensive curriculum
option and the smallest to graduates from the occupation specific curriculum
option. On the other hand, the evidence shows that these options benefit
low achievers, who remain at school, and acquire at least minimum employable
skills and avoid long-term unemployment. The evidence did not show differences
in earnings relative to type of curriculum completed, but it did show differences
relative to gender (females had lower earnings) and to type of employment
(i.e. self employment, civil servant, employer, etc.).
7. SCHOOL-TO-WORK
TRANSITION PERFORMANCE OF 'MALE', 'FEMALE' AND 'NEUTRAL' VOCATIONAL
STREAMS: A GENDER BALANCE SHEET FOR VOCATIONAL EDUCATION GRADUATES IN
GREECE,
(ZIP file in English) [published
in "Journal of Vocational Education and Training", Vol.
55, No 2, pp.209-221, 2003],
Stamatis Paleocrassas,
Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou
ABSTRACT
The issue of gender-related
differences in the transition of secondary vocational education graduates
from school-to-work is discussed, relative to 'male', 'female' and 'neutral'
curriculum choices, using findings from a national survey of graduates (1st Graduates Survey).
The discussion explores thiw issue using matched employment and earnings
as critical indicators. Comparisons are made with corresponding findings
in a survey conducted by CEREQ for France. This article suggests that gender
equity in entry and and transition to labour market is a complex issue,
when explored relative to gender related choices of vocational streams and
gender differences in transition performance. The findings where generally
consistent with expectations, relative to the social condext, which prevails
in Greece. The evidence supports the Frence conclusion that, under certain
conditions, non-traditional education and training can benefit young women
in their school-to-work transition. On the other hand, unlike the French
findings, data on some segregated training programmes show that female labour
market performance is suprisingly favourable, espesially for pre-vocational
training courses, which have a stronger general education component in the
curriculum than vocational education courses.
8. EDUCATIONAL
AND OCCUPATIONAL PREFERENCES OF MARITIME SECTOR STUDENTS,
(ZIP file
in Greek),
Stamatis
Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou, Athens 2001.
ABSTRACT
The scope of the research
was to identify the educational and occupational preferences of maritime
sector students of Greek Technical and Vocational Schools (TEE). The methodology
followed for the survey may be identified as a census type, since all 1st
and 2nd grade students (in total 338 students from 9 schools) of maritime
sector participated. A set of suggestions follows, based on the findings
and aiming at improving the curriculum, in order to match it better with
the needs of the students.

Β.
DROPOUTS IN SECONDARY EDUCATION
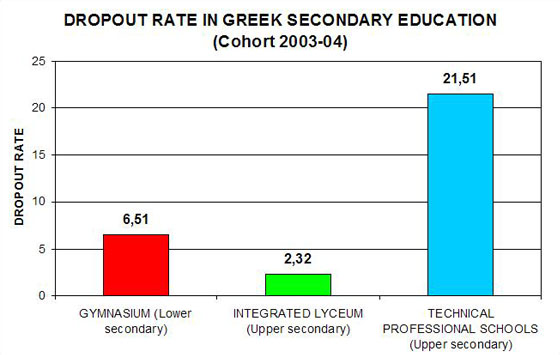
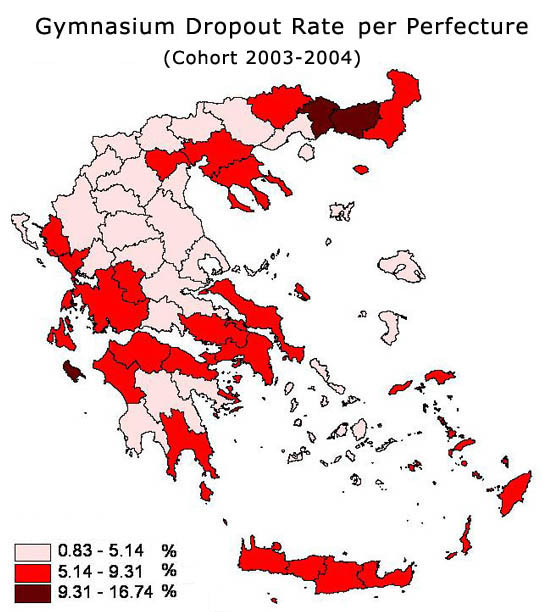
1. 4th DROPOUT SURVEY (COHORT 2003-04): DROPOUTS
IN SECONDARY EDUCATION (GYMNASIUM, INTEGRATED LYCEUM, TECHNICAL-PROFESSIONAL
SCHOOLS),
(ZIP file in Greek),
Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou, Athens 2008
Quantitative findings
of a survey on dropouts from all types of Greek secondary schools (Gymnasium,
Integrated Lyceum, Technical-Professional Schools) are presented and compared
with corresponding findings of previous dropout surveys and with relevant
findings from other european countries. The main finding of this survey is that the dropout rate decline in lower secondary education (as found out in previous dropout surveys) does not seem to continue. According to an estimation, which is based on the findings of this survey, the dropout rate for overall secondary education (lower and upper) adds up to 14%. Although Greece, when comparing with other EU countries, ranks in middle position in secondary education dropout rate, the abovemention figure makes difficult for the country to reach the objective set by European Council in 2003 (EC Objective: By 2010, an average ratio of no more than 10% early school leavers should be achieved).
2.
3th Dropout Survey (cohort 2000-01): DROPOUTS
IN SECONDARY EDUCATION (GYMNASIUM, INTEGRATED LYCEUM, TECHNICAL-PROFESSIONAL
SCHOOLS),
(zip file in Greek),
Panagiotis Rouseas,
Vasileia Vretakou, Athens 2006
Quantitative findings
of a survey on dropouts from all types of Greek secondary schools (Gymnasium,
Integrated Lyceum, Technical-Professional Schools) are presented and compared
with corresponding findings of previous dropout surveys and with relevant
findings from other european countries. The
national average dropout rate has been found to be steadily declining.
3.
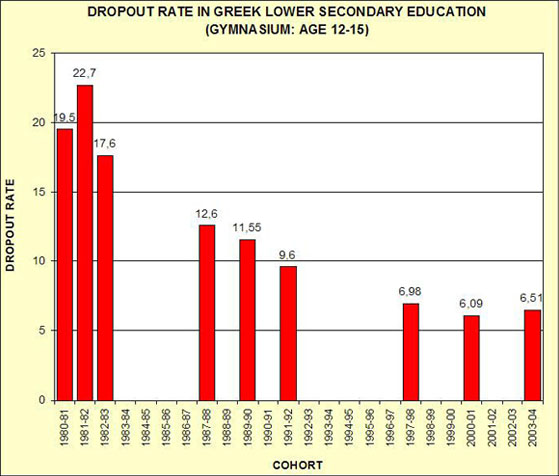
2th Dropout Survey (cohort 1997-98): DROPOUTS
IN GREEK LOWER SECONDARY EDUCATION (GYMNASIUM): QUANTITATIVE DATA,
(file in Greek),
Stamatis Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou,
Athens 2001.
Quantitative findings
of a survey on dropouts from the Greek lower secondary school are presented
and compared with corresponding findings of ten and twenty years ago. The
national average dropout rate has been found to be steadily declining, when
compared with the respective findings of previous dropout surveys.
4. 1th
Dropout Survey (cohorts 1987-88, 1989-90, 1991-92): DROPOUTS IN GREEK
LOWER SECONDARY EDUCATION (GYMNASIUM) AND THEIR NEEDS FOR VOCATIONAL
EDUCATION AND TRAINING: QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DATA ,
Stamatis
Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou, Athens 1996.
The following articles
(5, 6, 7) are based on data from 1st Dropout Survey.
5. DROPOUTS IN GREEK LOWER SECONDARY EDUCATION (GYMNASIUM):
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DATA (pdf file in Greek),
(PDF file in Greek) [published in the Proceedings of the European Symposium for the School
Failure (S. Paleocrassas, editor), pp. 68-76, Αthens 1997]
Stamatis Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou.
ABSTRACT
Quantitative and qualitative
data concerning Gymnasium dropouts are presented and commented upon. Based
on these empirical data and on similar data originated in other European
countries the authors argue that the average dropout rate in the Greek compulsory
education cycle is near the average rate in the European Union. Yet, when
linking this seemingly good statistic to the serious demographic problem
of Greece, an unpleasant reality is coming up. In a country where the birthrate-index
has fallen to 1.48, with the critical limit being 2, about 15,000 young
people exit the education system each year without any formal qualifications
and with limited prospects for proper jobs. On the other hand, according
to the survey findings, it is encouraging that most Greek Gymnasium dropouts
hold some sort of a job and do not exhibit antisocial behaviour. More importantly,
most of them are aware of their limited occupational prospects and are eager
to attend special vocational education and training courses in order to
improve themselves.
6. DESIGNING SPECIAL VOCATIONAL
TRAINING COURSES FOR SCHOOL DROPOUTS: THE CASE OF GREECE (htm file in
English),
(HTM file in English) [published in "International Journal of Vocational Education and Training",
Vol 5, No 2, pp. 57-64, Fall 1997]
Stamatis Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou.
ABSTRACT
Recent findings of a
survey type research showed that each year about 15,000 students drop out
of lower secondary education schools, before completing compulsory education.
Compulsory education in Greece does not contain a vocational training component
and, consequently, these young people are inducted into the world of work
without employable skills. Designing initial vocational training courses
for school dropouts is a procedure which requires the cooperation of several
specialists, each one of whom must be experienced in addressing special
needs. Following the research findings in Greece, these needs are councelling,
vocational orientation and guidance, modularized curriculum development
based on the learning-by-objectives method, and local labour market analysis.
The procedure also needs some validation and consensus by the local social
partners, if the outcome of the training delivery is to maximize the prospects
for stable employment for the dropouts. This paper proposes a framework
for the conceptualisation of such course designs, which may be useful to
other countries with similar socio-economic conditions.
7.
GREEK LOWER SECONDARY DROPOUTS: RESULTS FROM A NATIONAL STUDY,
(PDF
file in English), [published in "Journal
of the European Educational Research Association", Volume 3, Number
1, April 1997, pp. 12-18],
Stamatis Paleocrassas, Panagiotis Rouseas, Vasileia Vretakou
ABSTRACT
Quantitative and qualitative
data are used to compare the recent dropout rates in Greek secondary education
with the situation ten years before and to examine the factors contributing
to this dropout. The authors suggest that the principle reasons for dropout
lie in low school achievement coupled with economic or domestic demands
within the family. Unlike many western european countries, little association
was found between dropping-out of school and anti-social behaviour.

C.
MISCELLANIOUS SURVEYS - STUDIES
1. RESEARCH
ON THE LINKING OF VOCATIONAL EDUCATION AND TRAININIG CURRICULA WITH
THE LABOUR MARKET,
Athens 2008 (PDF file in Greek)
ABSTRACT
The study involves a pilot application of a model, which is being used by the German research center BIBB for the linking of vocational education curricula with the labour market. The model concerns the establishment of a labour market network of 'correspondents', according to economic sectors, aiming at gathering critical information concerning developments in job contents, and thereby updating accordingly the related curricula contents.
The network of labour market correspondents is expected to fill the deficit in work experience of the curriculum developers at the Pedagogical Institute, who, by law, are hired primarily on the basis of their scientific qualifications.
The study also explores the method of selecting the proper correspondents and the way of creating a related Register, from which the curriculum developers at the Pedagogical Institute will be selecting, experienced advisers, individually or in Ad Hoc project teams, so that the curricula under development would be unofficially validated by labour market practioners, before they are finalized and implemented.
2. RESEARCH
ON THE EDUCATIONAL CHOICES OF SECONDARY EDUCATION STUDENTS IN RELATION
WITH THE TERTIARY EDUCATION DEPARTMENT THEY ADMITTED THROUGH "PANELLENIC
ENTRANCE EXAMINATIONS",
(ZIP file in Greek) Christos
Ragiadakos, Athens 2008
3. SUPPLY AND DEMAND COUNTER-BALANCE TECHNIQUES OF EDUCATIONAL CHOICES IN EUROPE,
(ZIP file in Greek) Christos
Ragiadakos, Athens 2008
4. VOCATIONAL
EDUCATION AND TRAINING IN GREECE (SHORT DESCRIPTION),
(PDF
file in English) [This
study was commisioned and printed by CEDEDOP], September
2002,
Vasileia Vretakou, Panagiotis Rouseas,

D. POLICY PAPERS
1. POLICY
PAPER BASED ON THE "RESEARCH ON THE LINKING OF VOCATIONAL EDUCATION
AND TRAININIG CURRICULA WITH THE LABOUR MARKET,
Stamatis Paleocrassas, Athens 2008, (ZIP file
in Greek)
2. POLICY
PAPER BASED ON THE "2nd GRADUATES SURVEY",
Stamatis Paleocrassas, Athens 2007, (ZIP
file in Greek)
3. POLICY
PAPER BASED ON THE "4th Dropout Survey (cohort 2003-04): DROPOUTS
IN SECONDARY EDUCATION (GYMNASIUM, INTEGRATED LYCEUM, TECHNICAL-PROFESSIONAL
SCHOOLS)",
Stamatis Paleocrassas, Athens 2007, (ZIP file in Greek)

|
